AP
APOC3-mediated dyslipidemia in kidney disease and atherosclerosis in diabetes
Jenny Kanter
NIDDK

Be
Best Case Worst Case: Effective Communication between Kidney Specialists and Their Patients
Daniel Lam
NIH
CA
CAP: Community Acquired Pneumonia Study
Pavan Bhatraju
NIDDK
Ch
Characterization of the Impact of Cortisol on Kidney Clearance
Edward J. Kelly
Drug Design/Metabolism/…
CO
CONCORD: Combination of Novel Therapies for CKD Comorbid Depression
Rajnish Mehrotra
NIDDK

Ex
Extended Longevity of 3D Tissues and Microphysiological Systems for Modeling of Acute and Chronic Exposures to Stressors
Cathy Yeung
NASA
Im
Improving Medical Decision Making for Older Patients with End Stage Renal Disease
Susan Wong
Ki
Kidney Tubular Functions in Type 1 Diabetes
Ian de Boer
NIDDK
KT
KTE-PREM (Kidney transplant evaluation patient reported experience measure)
Kate Butler, MD, MA
NIDDK

OK
OK-D: Association between retinal angiography findings and kidney histopathology in participants with diabetes
Christine Limonte

PE
PERLage: Preventing Early Renal Loss in Diabetes
Ian de Boer
Joslin Diabetes Center (Flow…
Pr
Promoting goal concordant care among patients with advanced kidney disease
Susan Wong
RE
REMODEL-T1D
Ian de Boer
Breakthrough T1D
RO
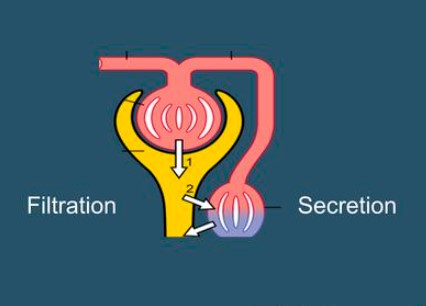
ROKIT: Role of Kidney Tubular Secretion in Critical Illness
Bryan Kestenbaum
NIDDK
Ro
Role of inflammation in intraplaque hemorrhage pathogenesis
Jenny Kanter
Nat'l Heart Lung &…

Th
The Role of the Complement System in Renal Cell Carcinoma
Christopher Blosser
Andy Hill CARE Fund
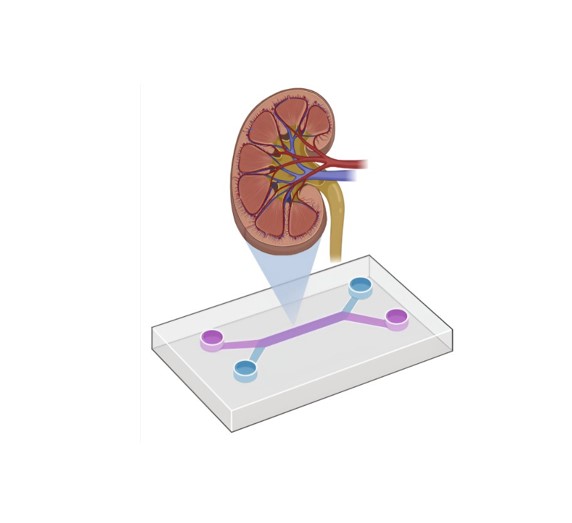
Tr
Translational Center for Kidney Microphysiological Systems to Improve Drug Safety and Efficacy (TraCe MPS)
Edward J. Kelly
NCATS