BOLD: Blood Pressure Lowering In Dialysis Trial
Investigator
What is the BOLD Study?
25 Seattle area dialysis patients and 25 San Francisco dialysis patients took part in this study looking at the feasibility, safety, and efficacy of home versus in-center dialysis blood pressure goals.
Blood pressure is one of the most important and treatable risk factors to prevent cardiovascular disease and lower the risk of death. Patients with kidney failure (end-stage renal disease) treated with hemodialysis have a very high risk of cardiovascular disease and death. Patients on hemodialysis are unique in that they can have blood pressure taken in different settings, including at the start of dialysis treatment (in the dialysis unit), at a regular doctor’s office visit, or at home (outside of the dialysis unit). However, it remains unknown which of these blood pressures is the best target for treatment in this population.
The purpose of this pilot study was to test if it is possible to adjust dry weight and blood pressure medication to achieve systolic blood pressure <140 mmHg among hemodialysis patients measured in two different settings–at the dialysis unit or home. We hope this pilot study will lead to a larger-scale study to examine whether such different blood pressure management will improve clinical outcomes.
Results:
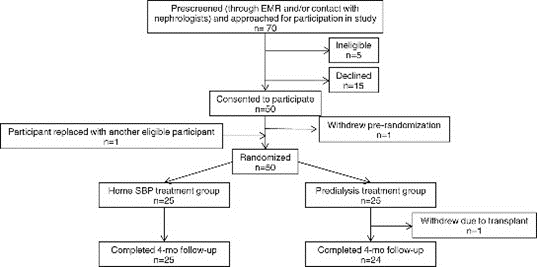
50 of 70 (71%) patients who were approached agreed to participate. All enrollees completed the study except for 1 who received a kidney transplant. In the home BP treatment group, adherence to obtaining/reporting home BP was 97.4% (and consistent over the 4 months). There was no increased frequency of high (defined as SBP > 200 mm Hg; 0.2% vs 0%) or low (defined as <90 mm Hg; 1.8% vs 1.2%) predialysis BP readings in the home versus predialysis treatment arms, respectively. However, participants in the home BP arm had higher frequency of fatigue (32% vs 16%). This pilot trial demonstrates feasibility and high adherence to home BP measurement and treatment in hemodialysis patients.
Findings:
This pilot trial shows a high home blood pressure measurement rate among participants. This demonstrates that treatment of home blood pressure in hemodialysis patients may be safe and effective but further studies are needed.
Publications:
"Treating Home Versus Predialysis Blood Pressure Among In-Center Hemodialysis Patients: A Pilot Randomized Trial"